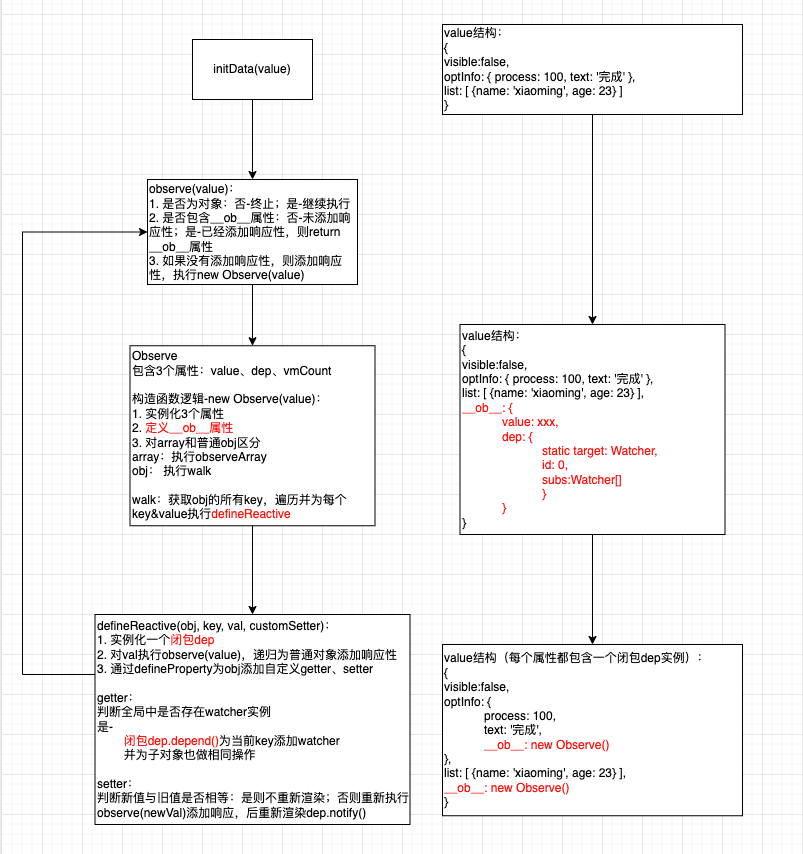
响应式原理
Vue的响应式原理由三部分组成,分别是:
- Observer(生产方): 数据拦截,添加响应性
- Dep(消息中心): 消息发布方
- Watcher(消费方): 消息订阅方
Observer
只有没有添加过响应性才会实例化Observer。Observer的作用是为data中的属性添加响应性
/**
* Observer class that are attached to each observed
* object. Once attached, the observer converts target
* object's property keys into getter/setters that
* collect dependencies and dispatches updates.
*/
export class {
value: any;
dep: Dep; // 每一个Data的属性都会绑定一个dep,用于存放watcher arr
vmCount: number; // number of vms that has this object as root $data
constructor(value: any) {
this.value = value
this.dep = new Dep()
this.vmCount = 0
def(value, '__ob__', this) // 为value添加__ob__属性,值为当前Observer实例
if (Array.isArray(value)) {
/*
区分数组,数组的处理方式是代理数组能修改自身的方法,如:splice、push、pop等
*/
const augment = hasProto
? protoAugment /*直接覆盖原型的方法来修改目标对象*/
: copyAugment /*定义(覆盖)目标对象或数组的某一个方法*/
augment(value, arrayMethods, arrayKeys)
/*如果是数组则需要遍历数组的每一个成员进行observe*/
this.observeArray(value)
} else {
/*如果是对象则直接walk进行绑定*/
this.walk(value)
}
}
/**
* Walk through each property and convert them into
* getter/setters. This method should only be called when
* value type is Object.
*/
walk(obj: Object) {
const keys = Object.keys(obj)
/*
遍历对象的每一个key,并调用defineReactive代理getter和setter
*/
for (let i = 0; i < keys.length; i++) {
defineReactive(obj, keys[i], obj[keys[i]])
}
}
/**
* Observe a list of Array items.
*/
observeArray(items: Array<any>) {
/*
数组需要遍历每一个成员进行observe
*/
for (let i = 0, l = items.length; i < l; i++) {
observe(items[i])
}
}
}Dep
每个属性都会包含一个闭包dep,但是每个引用数据类型又都对应一个dep。所以属性与dep的对应关系是:
- 引用类型:2个dep
- 基本类型:一个闭包dep
dep的作用是消息生产者,也是消息发布方。
/**
* A dep is an observable that can have multiple
* directives subscribing to it.
*/
export default class Dep {
static target: ?Watcher; // 全局的watcher,同一时间只会存在一个watcher
id: number; // dep的唯一标识,用于去重
subs: Array<Watcher>; // 存放dep对应的watcher
constructor() {
this.id = uid++;
// subs: Array<Watcher>
this.subs = [];
}
/*添加一个订阅方*/
addSub(sub: Watcher) {
this.subs.push(sub);
}
/*移除一个订阅方*/
removeSub(sub: Watcher) {
remove(this.subs, sub);
}
depend() {
if (Dep.target) {
// Dep.target指向的是一个watcher,
// 全局中存在watcher时,会调用watcher的addDep添加dep
// dep与watcher两者的关系,两者互相依赖:dep -> watcher watcher -> dep
Dep.target.addDep(this);
}
}
/*通知所有订阅方*/
notify() {
// stabilize the subscriber list first
const subs = this.subs.slice();
for (let i = 0, l = subs.length; i < l; i++) {
// 调用每一个watcher的update
subs[i].update();
}
}
}
// the current target watcher being evaluated.
// this is globally unique because there could be only one
// watcher being evaluated at any time.
// 全局watcher用完即丢
Dep.target = null;Watcher
watcher是消息订阅方,在vue中watcher分为3中:render watcher、computed watcher、user watcher
export default class Watcher {
vm: Component;
expression: string; // 每一个DOM attr对应的string
cb: Function; // update的时候的回调函数,对应option中watch的handler
id: number;
deep: boolean; // 是否深度监听,对应对应option中watch的deep
user: boolean; // 标识为用户自定义watcher
lazy: boolean; // 是否
sync: boolean; // 是否为同步执行的
dirty: boolean; // 是否为脏数据,脏检查位
active: boolean;
deps: Array<Dep>; // watcher对应的依赖新deps
newDeps: Array<Dep>; // 旧deps
depIds: ISet; // 去重后的旧dep实例的id
newDepIds: ISet; // 去重后的新dep实例的id
getter: Function; // watcher对应函数,执行的结果为this.value
value: any; // getter返回值
constructor(vm: Component, expOrFn: string | Function, cb: Function, options?: Object) {
this.vm = vm;
/*组件属性中_watchers存放所有订阅者实例*/
vm._watchers.push(this);
if (options) {
this.deep = !!options.deep;
this.user = !!options.user;
this.lazy = !!options.lazy;
this.sync = !!options.sync;
} else {
this.deep = this.user = this.lazy = this.sync = false;
}
this.cb = cb;
this.id = ++uid; // uid for batching
this.active = true;
this.dirty = this.lazy; // for lazy watchers
this.deps = [];
this.newDeps = [];
this.depIds = new Set();
this.newDepIds = new Set();
this.expression = process.env.NODE_ENV !== 'production' ? expOrFn.toString() : '';
// parse expression for getter
/* 把表达式expOrFn解析成getter */
if (typeof expOrFn === 'function') {
this.getter = expOrFn;
} else {
this.getter = parsePath(expOrFn);
if (!this.getter) {
this.getter = function () {};
process.env.NODE_ENV !== 'production' &&
warn(
`Failed watching path: "${expOrFn}" ` +
'Watcher only accepts simple dot-delimited paths. ' +
'For full control, use a function instead.',
vm,
);
}
}
this.value = this.lazy ? undefined : this.get();
}
/**
* Evaluate the getter, and re-collect dependencies.
*/
get() {
// 将Dep.target指向自身
pushTarget(this);
let value;
const vm = this.vm;
if (this.user) {
// 用户自定义的watcher需要try...catch
try {
value = this.getter.call(vm, vm);
} catch (e) {
handleError(e, vm, `getter for watcher "${this.expression}"`);
}
} else {
// 内置的watcher可信,无需try...catch
value = this.getter.call(vm, vm);
}
if (this.deep) {
traverse(value);
}
// 删除Dep.target
popTarget();
// 清除当前watcher的部分dep,以及移除dep中watcher。相当于移除弃用的watcher和dep的关系
this.cleanupDeps();
return value;
}
/**
* Add a dependency to this directive.
*/
// 保存dep到deps中
addDep(dep: Dep) {
const id = dep.id;
if (!this.newDepIds.has(id)) {
// 防止newDepIds有重复的dep实例id
this.newDepIds.add(id);
this.newDeps.push(dep);
if (!this.depIds.has(id)) {
// 订阅dep
dep.addSub(this);
}
}
}
/**
* Clean up for dependency collection.
*/
cleanupDeps() {
/*移除所有观察者对象*/
let i = this.deps.length;
while (i--) {
const dep = this.deps[i];
if (!this.newDepIds.has(dep.id)) {
// 如果当前watcher中的依赖中不包含了dep,那么dep移除当前watcher实例
dep.removeSub(this);
}
}
// 交换了depIds和newDepIds
let tmp = this.depIds;
this.depIds = this.newDepIds;
this.newDepIds = tmp;
// 清除newDepIds
this.newDepIds.clear();
// 交换deps和newDeps
tmp = this.deps;
this.deps = this.newDeps;
this.newDeps = tmp;
// 清空newDeps
this.newDeps.length = 0;
}
/**
* Subscriber interface.
* Will be called when a dependency changes.
*/
// 依赖改变时,会调用notify通知watcher执行update方法
update() {
/* istanbul ignore else */
if (this.lazy) {
this.dirty = true;
} else if (this.sync) {
this.run();
} else {
// 将watcher放到队列中
queueWatcher(this);
}
}
/**
* Scheduler job interface.
* Will be called by the scheduler.
*/
// 放入队列的watcher会去执行run方法
run() {
if (this.active) {
const value = this.get();
if (
value !== this.value ||
// Deep watchers and watchers on Object/Arrays should fire even
// when the value is the same, because the value may
// have mutated.
/*
即便值相同,拥有Deep属性的观察者以及在对象/数组上的观察者应该被触发更新,因为它们的值可能发生改变。
*/
isObject(value) ||
this.deep
) {
// set new value
const oldValue = this.value;
/*设置新的值*/
this.value = value;
/*触发回调渲染视图*/
if (this.user) {
try {
this.cb.call(this.vm, value, oldValue);
} catch (e) {
handleError(e, this.vm, `callback for watcher "${this.expression}"`);
}
} else {
this.cb.call(this.vm, value, oldValue);
}
}
}
}
/**
* Evaluate the value of the watcher.
* This only gets called for lazy watchers.
*/
/*获取观察者的值*/
evaluate() {
this.value = this.get();
this.dirty = false;
}
/**
* Depend on all deps collected by this watcher.
*/
/*收集该watcher的所有deps依赖*/
depend() {
let i = this.deps.length;
while (i--) {
this.deps[i].depend();
}
}
/**
* Remove self from all dependencies' subscriber list.
*/
/*将自身从所有依赖收集订阅列表删除*/
teardown() {
if (this.active) {
// remove self from vm's watcher list
// this is a somewhat expensive operation so we skip it
// if the vm is being destroyed.
/*从vm实例的观察者列表中将自身移除,由于该操作比较耗费资源,所以如果vm实例正在被销毁则跳过该步骤。*/
if (!this.vm._isBeingDestroyed) {
remove(this.vm._watchers, this);
}
let i = this.deps.length;
while (i--) {
this.deps[i].removeSub(this);
}
this.active = false;
}
}
}render watcher
在执行渲染watcher之前,vue首先将template编译成render函数,并且在执行vm.$mount时实例化渲染watcher,其中构造参数为:
new Watcher(
vm,
() => {
vm._update(vm._render(), hydrating);
},
noop,
watcherOptions,
true /* isRenderWatcher */,
);执行get函数时,会所有在template中使用的依赖都会添加订阅方:渲染watcher。
computed watcher
计算属性watcher,在initState时为每个computed属性实例化watcher。
initComputed执行时机需要晚于initData,原因是:
computed中的依赖必然都是来自data,而只有在为data中的属性添加完响应性时,computed和data之间的桥梁才可以建立
function initComputed(vm: Component, computed: Object) {
// $flow-disable-line
// 创建一个完全pure的对象
const watchers = (vm._computedWatchers = Object.create(null));
// computed properties are just getters during SSR
const isSSR = isServerRendering();
for (const key in computed) {
const userDef = computed[key];
const getter = isFunction(userDef) ? userDef : userDef.get;
if (__DEV__ && getter == null) {
warn(`Getter is missing for computed property "${key}".`, vm);
}
if (!isSSR) {
// 创建了内置的computed watcher,相应的也完成了发布和订阅
watchers[key] = new Watcher(vm, getter || noop, noop, computedWatcherOptions);
}
// ...
}
}user watcher
用户自定义的watcher主要有两个来源:
- 定义在options中watch
- this.$watch监听
但是它们最终都是去调用$watch去实例化一个watcher实例,并且返回一个unwatch函数,再不需要时调用。
// expOrFn 对应watch的key,cb对应handler
Vue.prototype.$watch = function (expOrFn: string | (() => any), cb: any, options?: Record<string, any>): Function {
const vm: Component = this;
if (isPlainObject(cb)) {
return createWatcher(vm, expOrFn, cb, options);
}
options = options || {};
options.user = true;
const watcher = new Watcher(vm, expOrFn, cb, options);
if (options.immediate) {
const info = `callback for immediate watcher "${watcher.expression}"`;
pushTarget();
invokeWithErrorHandling(cb, vm, [watcher.value], vm, info);
popTarget();
}
return function unwatchFn() {
watcher.teardown();
};
};简化流程
// 从initData中进入该方法,value对应options中的data返回值
export function observe(value: any, asRootData: ?boolean): Observer | void {
// 只为对象添加响应性,不是对象则中止流程
if (!isObject(value)) {
return;
}
let ob: Observer | void;
// __ob__标识value是否已经被添加了响应性
if (hasOwn(value, '__ob__') && value.__ob__ instanceof Observer) {
ob = value.__ob__;
} else if (
// 确保value类型为纯对象
observerState.shouldConvert &&
!isServerRendering() &&
(Array.isArray(value) || isPlainObject(value)) &&
Object.isExtensible(value) &&
!value._isVue
) {
// 创建一个Observer实例,进入Observer的构造方法中
ob = new Observer(value);
}
if (asRootData && ob) {
ob.vmCount++;
}
return ob;
}实例化Observer之后,会去执行walk方法,而它最终调用的是defineReactive:
export function defineReactive(obj: Object, key: string, val: any, customSetter?: Function) {
// 定义一个闭包dep对象
const dep = new Dep();
const property = Object.getOwnPropertyDescriptor(obj, key);
if (property && property.configurable === false) {
return;
}
// 获取自定义的getter和setter
// cater for pre-defined getter/setters
const getter = property && property.get;
const setter = property && property.set;
// 为value添加响应性,如果value为普通对象,则childOb为Observer实例;反之则为undefined
let childOb = observe(val);
Object.defineProperty(obj, key, {
enumerable: true,
configurable: true,
get: function reactiveGetter() {
const value = getter ? getter.call(obj) : val;
// get时判断当前全局中是否存在watcher
if (Dep.target) {
// 存在watcher则:为dep添加订阅方,为watcher添加发布方
dep.depend();
if (childOb) {
/*子对象进行依赖收集,其实就是将同一个watcher观察者实例放进了两个depend中,一个是正在本身闭包中的depend,另一个是子元素的depend*/
childOb.dep.depend();
}
if (Array.isArray(value)) {
dependArray(value);
}
}
return value;
},
set: function reactiveSetter(newVal) {
const value = getter ? getter.call(obj) : val;
// 如果新值和旧值相同则不重新渲染,这只对基本数据类型有效
/* eslint-disable no-self-compare */
if (newVal === value || (newVal !== newVal && value !== value)) {
return;
}
/* eslint-enable no-self-compare */
if (process.env.NODE_ENV !== 'production' && customSetter) {
customSetter();
}
if (setter) {
setter.call(obj, newVal);
} else {
val = newVal;
}
// 对新值添加响应性
childOb = observe(newVal);
// 通知订阅方重新渲染
dep.notify();
},
});
}
综上,为了便于理解,我们可以将watcher看成数学概念中的:f(x1, x2, x3, ...),其中dep为x1,x2,x3...
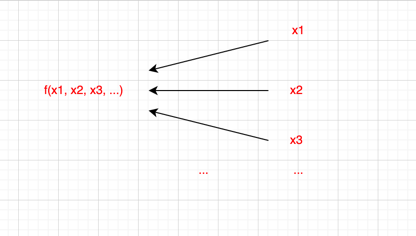
f(x1, x2, x3, ...)的值依赖x1, x2, x3, ... ,所以当依赖发生改变时,需要通知(也就是调用notify通知watcher执行get函数)f(x1, x2, x3, ...) 重新执行获取最新的值。
但是会有多个依赖存在相同watcher的情况,所以放到队列中时需要去重防止重复执行
数据拦截两种方式对比
Object.defineProperty
定义个体的行为
// Object
let obj = {};
Object.defineProperty(obj, 'name', {
get() {
return 1;
},
set(value) {
console.log('>>>>value:' + value);
},
});
// Array 数据拦截较为复杂,vue重写了array的api
let arr = [1, 2, 3];
Object.defineProperty(arr, 3, {
get() {
return 1;
},
set(value) {
console.log('>>>>value:' + value);
},
});
es6提供的Proxy
定义整体的行为
// Object
let obj = {};
let proxyObj = new Proxy(obj, {
get() {
return 1;
},
set(value) {
console.log('value:' + value);
},
});